Bhuvan's Blog
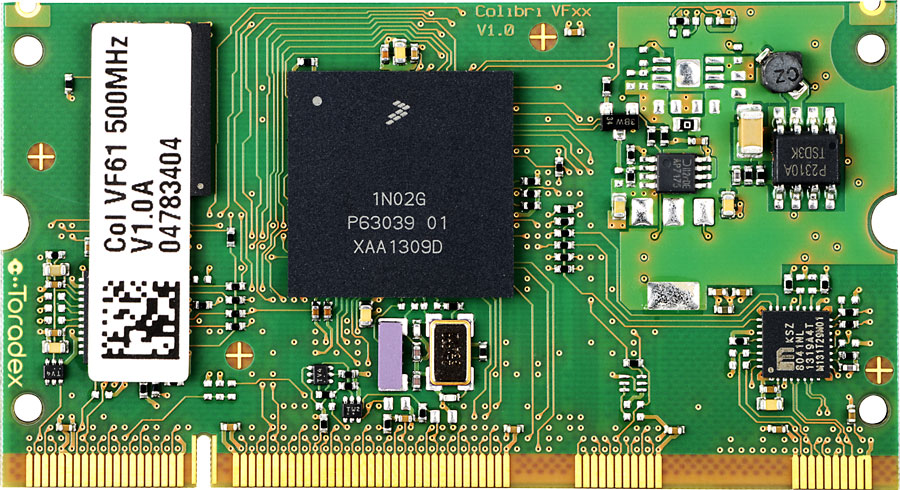
The Colibri VF50 and VF61 are both SODIMM sized computer modules based on the Qualcomm/NXP/Freescale Vybrid embedded System-on-Chip (SoC). The Vybrid SoC features a Cortex-A5 processor supporting a clock frequency of up to 500MHz. The Colibri VF61 additionally features a second Cortex-M4 processor core which can be clocked at up 167MHz maximum.
This unique heterogeneous dual core system allows for running a second hard real time operating system on the M4 core for time and security critical tasks. The module tarets a wide range of applications, including: Digital Signage, Medical Devices, Navigation, Industrial Automation, HMIs, Avionics, Entertainment System, POS, Data Acquisition, Thin Clients, Robotics, Gaming and many more. It offers a wide range of interfaces from simple GPIOs, industry standard I2C and SPI buses through to high speed USB 2.0 interfaces.
Both Colibri VFxx modules feature a Fast Ethernet PHY with IEEE1588 time stamping on the module. Additional, a second PHY can be integrated on the customer carrier board by using the RMII interface. Existing customers will benefit from an extremely easy migration path from the current Colibri PXAxxx or Colibri T20/30 module range to the Colibri VFxx – all Colibri modules are electrically pin compatible.
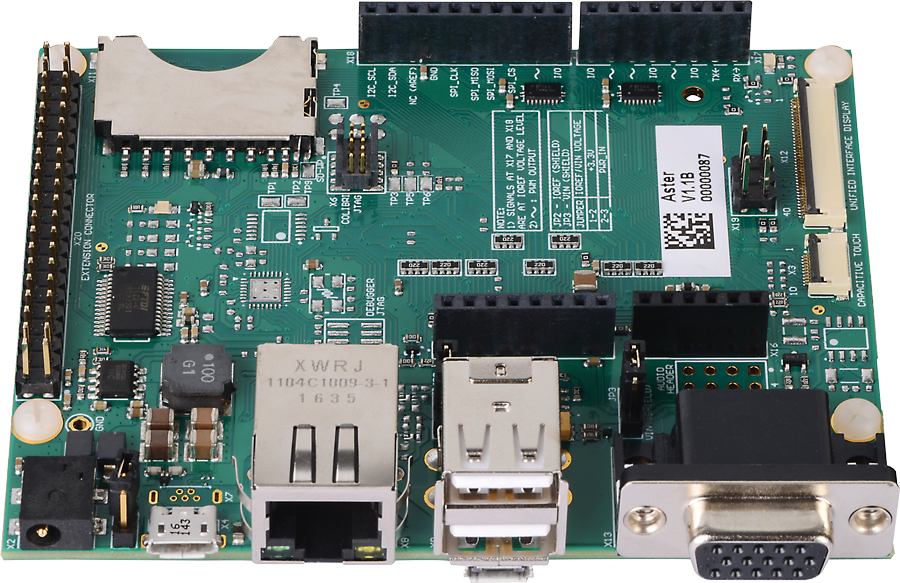
Carrier board for Toradex Colibri System on Module Family. Good thing about this board is the availability of Arduino Uno and Raspberry Pi expansion headers, which means one can use any of the available Arduino/Rpi cape/add-on/hat Boards on this carrier board.
As Colibri Modules are electrically pin compatible, all the modules in Colibri Family can be used. In this example project we use Colibri VF61.


Build and install the OE-Core aka Yocto SDK, for instructions related to building and installing SDK, have a look at this knowledge base article. After installing SDK, cross-compile libsoc.
Cross-compiling libsoc:
$ cd ~/
$ git clone -b master https://github.com/jackmitch/libsoc.git
$ cd libsoc
$ . /usr/local/oecore-x86_64/environment-setup-armv7at2hf-neon-angstrom-linux-gnueabi
$ echo $CC
arm-angstrom-linux-gnueabi-gcc -march=armv7-a -mthumb -mfpu=neon -mfloat-abi=hard --sysroot=/usr/local/oecore-x86_64/sysroots/armv7at2hf-neon-angstrom-linux-gnueabi
$ autoreconf -i
$ ./configure --host=arm-angstrom-linux-gnueabi --prefix=/usr/local/oecore-x86_64/sysroots/armv7at2hf-neon-angstrom-linux-gnueabi/
...
$ make -j3
$ sudo make install
Cross-compiling libsoc examples:
$ cd ~/
$ git clone https://github.com/bhuvanchandra/libsoc-examples.git
$ cd libsoc-examples
$ cd ssd1306/
$ MACHINE=colibri-vf make
Copy the binary to target via ssh and run the example.
NOTE: One can build libsoc with Open Embedded aka Yocto. Recipe for libsoc is available with Open Embedded.